Difference between revisions of "1127: Congress"
m (→U.S. Federal Government: linking to the Apportionment Act of 1911) |
(It does feature Joe Biden (as thin line "other noteworthy members of Congress", not as dashed line "Future or past president". But still)) |
||
| (68 intermediate revisions by 39 users not shown) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
| date = October 29, 2012 | | date = October 29, 2012 | ||
| title = Congress | | title = Congress | ||
| + | | before = [[#Explanation|↓ Skip to explanation ↓]] | ||
| image = congress.png | | image = congress.png | ||
| − | |||
| titletext = It'd be great if some news network started featuring partisan hack talking heads who were all Federalists and Jacksonians, just to see how long it took us to catch on. | | titletext = It'd be great if some news network started featuring partisan hack talking heads who were all Federalists and Jacksonians, just to see how long it took us to catch on. | ||
}} | }} | ||
| − | Click the date above the comic to go to the xkcd page, and there is a link to the much larger version | + | Click the date above the comic to go to the xkcd page, and there is a link to the [http://xkcd.com/1127/large/ much larger version]. |
==Explanation== | ==Explanation== | ||
| − | It appears that the {{w|United States presidential election, 2012|upcoming 2012 election}} has put [[Randall]] into a political state of mind, as this is the second comic in a few weeks that has dealt with political history ([[1122: Electoral Precedent]]). As with that comic, this comic goes through the entire history of the {{w|Federal government of the United States|U.S. Federal Government}}. Also notably, Randall makes a number of observations that are akin to the type of observations Randall denounces in 1122 (e.g. for 1928, Randall notes that no Republican has since won the presidency without a Nixon or a Bush on the ticket). | + | It appears that the (at the time) {{w|United States presidential election, 2012|upcoming 2012 election}} has put [[Randall]] into a political state of mind, as this is the second comic in a few weeks that has dealt with political history ([[1122: Electoral Precedent]]). As with that comic, this comic goes through the entire history of the {{w|Federal government of the United States|U.S. Federal Government}}. Also notably, Randall makes a number of observations that are akin to the type of observations Randall denounces in 1122 (e.g. for 1928, Randall notes that no Republican has since won the presidency without a Nixon or a Bush on the ticket). Just around the election he posted two more comics related to this: [[1130: Poll Watching]] and [[1131: Math]]. |
===U.S. Federal Government=== | ===U.S. Federal Government=== | ||
| − | In the {{w|Federal government of the United States|U.S. Federal Government}}, one of the {{w|Separation of powers|checks and balances}} is a {{w|bicameralism|bicameral}} {{w|United States Congress}}, which consists of two "houses": the {{w|United States Senate|Senate}}, its "upper" house; and the {{w|United States House of Representatives|House of Representatives}} ("the House"), its "lower house". The Senate consists of 2 senators elected from each state (thus 100 total), while the House consists of 435 voting representatives (a number decided upon in {{w|Apportionment Act of 1911|1911}} by law) whose {{w|United States congressional apportionment|apportionment}} is split between the states proportional to their population; although each state gets at least one (the House also has non-voting representatives from | + | In the {{w|Federal government of the United States|U.S. Federal Government}}, one of the {{w|Separation of powers|checks and balances}} is a {{w|bicameralism|bicameral}} {{w|United States Congress}}, which consists of two "houses": the {{w|United States Senate|Senate}}, its "upper" house; and the {{w|United States House of Representatives|House of Representatives}} ("the House"), its "lower house". The Senate consists of 2 senators elected from each state (thus 100 total), while the House consists of 435 voting representatives (a number decided upon in {{w|Apportionment Act of 1911|1911}} by law) whose {{w|United States congressional apportionment|apportionment}} is split between the states proportional to their population; although each state gets at least one (the House also has non-voting representatives from non-state territories like {{w|Puerto Rico}} and the {{w|District of Columbia}}). Every ten years, the House is reapportioned based on the latest census. The most populous state as of 2012 is California which has 53 seats in the House. Senators serve 6-year terms with elections held every 2 years for one-third of the seats. Members of the House (called Representatives or Congressmen/women) serve 2-year terms with all of the seats contested every 2 years. |
| − | In order for a bill to become a law, it must be passed by both the House and the Senate. In a way, this theoretically ensures that the bill is supported both by the majority of states (the Senate), and the majority of the population (the House). The President may then sign the bill into law, | + | In order for a bill to become a law, it must be passed by both the House and the Senate. In a way, this theoretically ensures that the bill is supported both by the majority of states (the Senate), and the majority of the population (the House). The President may then sign the bill into law, he may "veto" the bill, or he may do nothing, in which case it becomes a law if and only if Congress is in session after a waiting period of 10 days (not including Sundays). |
===Political ideologies=== | ===Political ideologies=== | ||
| − | In politics, there is a {{w|political spectrum|scale}} that represents the political beliefs of a politician. The scale goes from "{{w|Left-wing politics|left}}" to "{{w|Right-wing politics|right}}" of "center" | + | In politics, there is a {{w|political spectrum|scale}} that represents the political beliefs of a politician. The scale goes from "{{w|Left-wing politics|left}}" to "{{w|Right-wing politics|right}}" of "center" — which generally describes a balancing point of beliefs (sometimes called "left-wing" or "right-wing"). |
| − | The "left" is a general belief in social justice, and is sometimes associated with {{w|socialism}} Modern left-wingers generally | + | The "left" is a general belief in social justice, and is sometimes associated with {{w|socialism}}. Modern left-wingers generally prioritize equality, and support policies like welfare and government-subsidized healthcare. This trends toward having a larger federal government. In the U.S., "liberal" is a term often used to denote left-leaning tendencies. |
| − | The "right" generally believe in | + | The "right" generally believe in personal responsibility and individual liberty, which is often termed {{w|conservatism|conservative}}. This trends towards having less regulation and thereby a smaller federal government. The goal is to keep the nation stable, and reducing the interference by the government with a person's wealth. This ostensibly means lower taxes, because the government does not provide as much. |
| − | Politicians typically align themselves into groups of similar beliefs and positions called "parties". In the U.S., there have generally been two dominant parties | + | Politicians typically align themselves into groups of similar beliefs and positions called "parties". In the U.S., there have generally been two dominant parties, although there have been times where three or more parties have shared roughly equal influence and support. In today's politics (which is apparently known as (the second part of) the fifth era of political parties, or {{w|Fifth Party System}}, as noted on the outside edges of the comic) of the two current primary U.S. political parties, the {{w|Democrats}} are the left-leaning party, and the {{w|Republicans}} are the right-leaning party. The dominant parties are generally considered "moderate" in their left- or right-wing leanings, as either party appears to requires the support of a majority (or a few percent under) of voters to win. However, this is complicated by a process called gerrymandering where election boundaries are redrawn to allow a political advantage to the party currently in power. Thus a popular majority state wide or any ratio of votes to representatives will not necessarily be reflected in delegates awarded, an example being the Republicans' REDMAP 2012 report ([http://maddowblog.msnbc.com/_news/2013/01/21/16630863-virginia-republicans-move-for-permanent-majority]). Smaller parties often run candidates with more extreme views, but such candidates rarely win, due to a more limited number of possible supporters ensuring that even a relatively large minority would have zero chance of representation. (see {{w|Duverger's law}}). |
===The comic=== | ===The comic=== | ||
| − | The comic effectively consists of three separate charts: The left- and right-hand charts are the main charts; they represent the Senate and House respectively, and purport to show the left- and right-wing leanings of each legislature through U.S. history. There is a legend on the right that sets out fairly clearly how the charts work, but basically Randall has split each wing into three levels including the very moderate or "Center" right or left, and the more extreme or "Far" right or left, as well as the average left and right | + | The comic effectively consists of three separate charts: The left- and right-hand charts are the main charts; they represent the Senate and House respectively, and purport to show the left- and right-wing leanings of each legislature through U.S. history. There is a legend on the right that sets out fairly clearly how the charts work, but basically Randall has split each wing into three levels including the very moderate or "Center" right or left, and the more extreme or "Far" right or left, as well as the average left and right without prefix. A dotted yellow line represents the balance of power in each legislature, and white lines represent the leanings of certain notable people including presidents. |
| − | Some presidents are not indicated, because they were never senators or congressmen (most of these were state Governors, such as {{w|Bill Clinton|Clinton}}, {{w|George W. Bush|Bush}} and 2012 candidate {{w|Mitt Romney}}). As may be noted from the chart, {{w|Barack Obama}} is considered "left" while {{w|Paul Ryan}} is | + | Some presidents are not indicated, because they were never senators or congressmen (most of these were state Governors, such as {{w|Bill Clinton|Clinton}}, {{w|George W. Bush|Bush}} and 2012 candidate {{w|Mitt Romney}}). As may be noted from the chart, {{w|Barack Obama}} is considered "left" while {{w|Paul Ryan}} is considered "far right". It's also notable that the "center right" ideology appears to be completely eradicated from the House and is waning in the Senate (although a similar trend is shown around 1900 with the centrists making a comeback thereafter). |
On either side of these charts, there are descriptions or explanations for expansions and contractions of each ideological group. | On either side of these charts, there are descriptions or explanations for expansions and contractions of each ideological group. | ||
| Line 37: | Line 37: | ||
Finally, there's a little extra commentary on the right side, below the legend. | Finally, there's a little extra commentary on the right side, below the legend. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===The title text=== | ||
| + | The title text refers to two political parties in American history: the Federalists and the Jacksonians. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Note that this means the two parties are not strictly contemporaries. There are features of both the modern Republican and Democratic parties in each, so depending on the topic presented, it may take a long time to figure out that they are not these modern parties until the topic of discussion changes. They do, however, make a nice dichotomy. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The Federalists are one of the oldest political parties in American History. Federalists were seen as conservative in their time, and similarly to modern Republicans much of their support came from bankers and businessmen and they were committed to a fiscally sound and government, but on the flip side they favored a strong central government, regulation of industry, a national banking system, and were protectionistic. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The Jacksonian party is one of the four branches of the Democratic Party that developed during the political chaos after the Federalist party died out in the War of 1812. The Jacksonians were considered liberal for their time, they believed in one man, one vote, regardless of standing, and their mascot was a donkey and they're the ancestors of the modern Democratic Party, but on the flip side they did not want a strong national government and believed that the government should have limited impact in the regulation of industry, going so far as to end the bank of the United States, and were fiercely expansionistic. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Network news channels regularly feature {{w|Pundit|talking heads}}, supposed 'experts' who offer their opinion on the topical political stories. Where these talking heads are strongly aligned with a particular party, and are unconcerned with anything other than winning, they could be described as a {{w|Partisan|partisan}} {{w|Political hack| hacks}}. | ||
==Transcript== | ==Transcript== | ||
| + | {{incomplete transcript}} | ||
| + | <!-- | ||
| + | *This transcript is neither only a representation the visible text in the small image or all of the text in the full image. | ||
| + | *Since there is text visible all over even the small image it would be most relevant to have a full transcript. | ||
| + | **Or at least make a separate transcript page like for [[980: Money\Transcript]]. | ||
| + | **In the latter case this transcript below should then be reduced to only visible text in small image! | ||
| + | --> | ||
:A history of | :A history of | ||
:'''The United States Congress''' | :'''The United States Congress''' | ||
:Partisan and ideological makeup | :Partisan and ideological makeup | ||
| + | |||
| + | :[The comic is divided into three massive sections, SENATE, PRESIDENCIES, and HOUSE. Timelines run backwards down the page between each section. In the HOUSE and SENATE sections, shifting, curving red and blue areas of different brightness illustrate the shifting balance of power between "Members of Left-Leaning Parties" and "Members of Right-Leaning Parties". Under PRESIDENCIES, different administrations are labeled and wars are shaded in gray. There are notes throughout all sections.] | ||
| + | |||
| + | :[There are additional notes on the right.] | ||
| + | |||
| + | :LEGEND | ||
| + | ::''[Square containing ribbons of color merging upwards with larger areas]'': Branches join in when new members enter Congress and cause an ideological bloc to grow. (Note: If the new member is elected as another retires from the same ideological bloc, no change is shown.) | ||
| + | ::''[Square containing ribbons of color splitting off from larger areas]'': Branches split off when members leave Congress, causing their ideological bloc to shrink. (Note: If the new member is elected as another retires from the same ideological bloc, no change is shown.) | ||
| + | ::''[Square showing yellow dotted line crossing from red to blue area]'': The yellow line marks the midpoint, which indicates which side has control of the chamber. | ||
| + | ::''[Square in which curve briefly separates from blue area]'': If a bloc loses members in one election and gains them in the next, the exiting stream may rejoin. This does not necessarily mean the same people returned. | ||
| + | ::''[Square showing white dashed line labeled Lyndon Johnson on top of ribbon merging with main area]'': Future (and past) US Presidents who served in Congress are shown with white dashed lines. Other noteworthy members are shown with thin solid lines. | ||
| + | ::''[Square in which tinted area marked "Whig" sits over mix of red and blue areas]'': Tinted white outlines mark the approximate membership of some of the smaller political parties. | ||
| + | |||
| + | :HOW IDEOLOGY IS CALCULATED | ||
| + | ::Each member of Congress is assigned to an ideological category using DW-NOMINATE, a statistical system created by political scientists Keith Poole and Howard Rosenthal. This system rates each member of Congress's ideological position position [sic] based on their votes. | ||
| + | ::DW-NOMINATE is purely mathematical and involves no judgement on the content of bills. Instead, members of Congress are placed on a spectrum based on how consistently they vote together. | ||
| + | ::While people argue that ideology is many-dimensional, Poole and Rosenthal found that nearly all Congressional voting behavior - especially in the modern era - can be accurately predicted by using just one ideological variable. | ||
| + | ::This variable turns out to roughly correspond to position on the classic economic liberal/conservative spectrum. | ||
| + | ::Because members of Congress have served in overlapping terms with past members in a chain back to the first Congress, the system allows comparison of ideology across time - even accounting for individual members' ideological drift. (Note: Scores are comparable across time but not between chambers.) | ||
| + | ::For more detail, see Poole and Rosenthal's website, voteview.com. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <!-- Here is a OCR'ed transcript. It's pretty accurate, but needs some revision. Here it is: | ||
| + | A HISTORY OF THE UNITED STATES CONGRESS PARTISAN AND IDEOLOGICAL MAKEUP | ||
| + | The chart width on each side corresponds to the number of seats held by two groups of parties:7 I Seats held 1;77c=13'"' Seats held by I left-leaning parties right-leaning parties (e.g. Democratic. Green) (e.g. Republican. Constitution) I | ||
| + | • .T Left L .Lefte.to., Reit (300 to S00,• • Center Left (0 to -300 center', Center Rjght (0 to 300)• | ||
| + | ( | ||
| + | Color shows the ideological makeup of the two sides based on member DW-NOMINATE SCORES (see below for more) | ||
| + | SENATE | ||
| + | Members of Left-Leaning Parties | ||
| + | In the later years of the Bush Administration, Democrats regained control of the Senate in 2006, and won a larger majority in 2008 during the onset of the financial crisis. | ||
| + | • PAR , SYS | ||
| + | FOURTH PARTY SYSTEM | ||
| + | THIRD PARTY YST | ||
| + | A recession, combined with Eiesnhower Administration policies unpopular with labor unions, helped Democrats make huge Senate gains in the 1958 midterm election, | ||
| + | Ronald Reagaris commanding victory over Jimmy Carter helped bring Democratic support ,r Republican Senate candidates. | ||
| + | Amid Democratic chaos, Republicans gained five Senate seats in 1968 and Nixon narrowly won the presidency. | ||
| + | Anger over Democratic support for civil rights led to pro-Segregation southerners leaving the Democratic party. | ||
| + | The series of victories by R000velt's New Deal Coalition led to the most lopsided | ||
| + | Democrats elected in FDR's New Deal waves 4 included future president A-HarryTruman and labor 'rer advocate Robert Wagner. | ||
| + | 191 The w se legislatures.T | ||
| + | 1928 was the last year in which the Republican Party won the White House without a Bush or Nixon on the ticket. | ||
| + | Teddy R000velt, unhappy with his chosen successor (and apparently bored with not being president anymore) challenged President Taft for the 1912 Republican nomination. | ||
| + | gow | ||
| + | The return of Southern partisans who had left to join the Confederacy eventually gave the Democrats the political power to end Reconstruction and put in place segregationist Jim Crow laws. | ||
| + | The Republicans dominated national politics after the war, with Grover Cleveland 90e only Democrat elected president over a period of more than half a century. | ||
| + | Republicans gained Senate seats in 1888 from a number of recently-admitted states. | ||
| + | CIVIL*WAR When the South seceded following | ||
| + | Nconai UNIONIST | ||
| + | Lincoln's election, most Southern Senate seats were declared vacant. | ||
| + | SECOND PARTY YST | ||
| + | Senator Henry Clay, by skillfully negotiating compromises, is said to have singlehandedly held off the Civil War for 40 years. | ||
| + | Senator John C. Calhoun, with his fiery arguments that white slaveowners were the real oppressed minority, helped emcee it eventually happened. | ||
| + | This strange influx of candidates on the right to parties on the left is a sign of the complete collapse of the Federalists. | ||
| + | JohnTyler was a former Democrat who opposed the Whig platform.When he became Pi-esident after Harris., death, the Whigs revolted, and—without support from either party—he suffered political deadlock. | ||
| + | DEMOCRATS The Democratic Party was formed by the followers of Andrew Jackson, an outspoken, aggressive populist who got in a lot of duels. | ||
| + | They fought against elite and business interests and stuck up for the the little guy—as long as the little guy was white.With a natural base among poor southern farmers, the Democrats became the party of slavery. | ||
| + | The basic contradiction of a party of slaveowners ostensibly standing for egalatarianism would go unresolved until the late 20th century. The 18th Congress w.ta,s,echoaveorwtic.hWeimhaitnghiayddobemcionmanet | ||
| + | iftPRae tpU jbel iffcea rnssc:rf';:gpmeen'tecdrai tniO four warring factions. DEMOCRATIC-REPUBLICANS The Democratic-Republi cans (or "Jefferson ian Republicans") were the party formed by the anti-administration faction. | ||
| + | This chart places them provisionally on the left, although since they absorbed many pro-administration figures, their DW-NOMINATE average is very cloo to zero. | ||
| + | ANTI-ADMINISTRATION The anti-administration faction favored states' rights and farmers, and opposed what they saw as Hamilton's tendencies toward elitism and monarchism. | ||
| + | PRESIDENCIES Barack Obama | ||
| + | 2006-2004 | ||
| + | 2002-2000 | ||
| + | 1998-1996 | ||
| + | 1994-1992 | ||
| + | 1988 | ||
| + | 1.6 1984 | ||
| + | 1.2 1980 | ||
| + | 1938 1936 | ||
| + | 1 93 1 | ||
| + | George W. Bush. | ||
| + | Bill <LINTON | ||
| + | George H.VV. sewu BUSH. | ||
| + | Ronald REAGAN. | ||
| + | Jimmy CARTER Gerald FORD. | ||
| + | — | ||
| + | Richard NIXON. | ||
| + | Lyndon B. JOHNSON | ||
| + | John F KENNEDY | ||
| + | Dwight EISENHOWER. | ||
| + | Harry S •TRUMAN | ||
| + | Roo.. di...Re | ||
| + | (ROOSEVELT | ||
| + | 1906 1904 | ||
| + | 190 2 1900 | ||
| + | 1886 1884 | ||
| + | 1 882 1880 | ||
| + | 1866 1864 | ||
| + | 1862 1860 | ||
| + | Ig8 1856 | ||
| + | I 806 1804 | ||
| + | Calvin COOLIDGE. Warren G. HARDING. | ||
| + | Woodrow _II/11 WILSON | ||
| + | William Howard TAFT. | ||
| + | Theodore ROOSEVELT. | ||
| + | Mc Krt. assassinated | ||
| + | Benjamin HARRISON. | ||
| + | Grover CLEVELAND Chester A. ARTHUR' l'adrnesA. GARFIELD• Rutherford B. HAYES. | ||
| + | Ulysses S. | ||
| + | GRANT. | ||
| + | Andrew JOHNSON. | ||
| + | Abraham LINCOLN. | ||
| + | James (BUCHANAN | ||
| + | Franklin PIERCE | ||
| + | Millard FILLMORE. zachary TAYLOR. | ||
| + | James K. •POLK John TYLER. HARRISON• | ||
| + | Martin Van •BUREN | ||
| + | Andrew JACKSON | ||
| + | John Quincy ADAMS. | ||
| + | James •MONROE | ||
| + | james w"18'i MADISON | ||
| + | Thomas JEFFERSON | ||
| + | John ADAMS. | ||
| + | George WASHINGTON. | ||
| + | 2002 2000 | ||
| + | I 9 98 1996 | ||
| + | I 95, 1988 | ||
| + | I 9 86 1984 1980 1976 | ||
| + | 1972 1968 | ||
| + | I 9 66 1964 1960 | ||
| + | I9S8 1956 | ||
| + | I 9 SO 1948 | ||
| + | I 946 1944 | ||
| + | 1932 1928 1924 | ||
| + | 1922 1920 1916 1912 1908 | ||
| + | I 9 06 1904 1900 | ||
| + | 1 898 1896 | ||
| + | 1890 1888 | ||
| + | 1886 1884 1880 1876 1872 1868 | ||
| + | I 8 66 1864 1860 | ||
| + | I8S8 1856 | ||
| + | I 8 SO 1848 | ||
| + | 1832 1828 1824 1820 1816 1812 1808 | ||
| + | 1806 1804 1800 | ||
| + | 1796 | ||
| + | I 7 90 1788 | ||
| + | HOUSE | ||
| + | Members of Left-Leaning Parties Members of Right-Leaning Parties 311 320 | ||
| + | h Right | ||
| + | The Tea Party wave of 2010 helped House Republicans regain all the ground they had lost in 2006 and 2008 and then some. | ||
| + | The Democratic Party's gains in 2006 and 2008 came largely from centrist candidates in swing districts—the same ones who would -- be voted out in 20 I | ||
| + | Center | ||
| + | Democratic losses in 1994 came almost exclusively among centrists, leaving the left and far left blocs relatively untouched—a pattern which would continue in 2010 | ||
| + | Democrats gained a | ||
| + | While the size of the Republican majority didn't Np change very much during this period, its internal makeup did.The centrist bloc nearly vanished, and in every election from 1984 to 2004, the far right bloc grew. | ||
| + | Newt Gingrich's Republican Revolution of 1994 gave the GOP control of the House for the first time in 40 years. | ||
| + | With Ronald Reagan's election in 1980, Republicans regained the ground they lost afterWatergate. | ||
| + | number of-House oats | ||
| + | in the aftermath of the | ||
| + | Watergate scandal. | ||
| + | Democrats added seats in 1958 through wins in the Rust Belt and the gain of every seat in Connecticut's delegation. | ||
| + | The New Deal wave consisted almost entirely of centrist Democrats. Over the course of the 20th century, theo centrists generally lost ground to left and far-left Democrats—a slow motion version of the process that has happened more rapidly and completely among House Republicans. | ||
| + | Other than these few years after the war, the House was under Democratic control for the entire period from the Great Depression until the Republican Revolution of 1994. | ||
| + | Republicans gained seats in I 942, as they had in the late 9I0s, due to concern over American entanglement in a war in Europe. | ||
| + | The onset of the Great Depression sparked a huge backlash against the Republicans who had held power throughout the 1920s. | ||
| + | PROGRESSIVE '1 AND fARME LABOR PARTIES | ||
| + | After losing his bid for the nomination, Roosevelt ran as a third-party candidate, splitting the Republican vote and leading to Wil.n's victory and huge (albeit temporary) Democratic gains in the House. | ||
| + | The 1896 presidential contest, which pitted Democrat William Jennings Bryan against Republican William McKinley, was probably the most heated election in American history. | ||
| + | In 1882, Democrats won seats thanks to disapproval of a Republican Congress that seemed too friendly to industry. | ||
| + | POPULIST | ||
| + | The "Panic of 1893" economic depression led to Republicans winning the largest single landslide in Congressional history. John Clayton was elected after ing a first count t 1:fttlefIrtlunsg if:te h e | ||
| + | The Democrat of seats in I 880 but no *, swon a lot one seems really sure why. | ||
| + | was shot by an unidentified assassin. His ideological category is unknown. | ||
| + | 1 I | ||
| + | Disapproval of Grant's handing of the Panic of I 873 (an economic depression) led to Democrats winning control of the House for the first time since the war. | ||
| + | CIVIL*WAR | ||
| + | 4) | ||
| + | After most Southern represtatives left to join the Confederate Congitss, the Democrats who remained were defined by opposition to the war | ||
| + | REPUBLICANS The Republican Party formed around opposition to slavery. As the party of the North, it | ||
| + | and financial interests, i ndustrialization, and Puritan - influenced social reforms eventually culminating in the Pro hibiti on movement. | ||
| + | WHIGS The Whigs were supporters of business and markets, economic modernization, and social reform. | ||
| + | They ultimately collapod over the issue of slavery, with the abolitionist faction eventually becoming the Republican Party. | ||
| + | The factions created by the .h ism in the Ion Congress then rejoined into a chaotic series of new parties, some only lasting one term. with Alexander Hamilton and administration faction allied ADMINISTRATION The pro-administration faction favored a central bank, and relaxed relations with party formed from the pro-George Washi ngton. sound national fiscal policy, Great Britain. PRO-FEDERALISTS The Federalists were the | ||
| + | LEGEND | ||
| + | Congress and cause an ideological bloc to grow rZtnill7d=o= C'nongre'ess.s Taliturg'theireniderftm'rological=to striik LIM it,'Ithetirem=7:::To"17ww7 | ||
| + | , WHIG | ||
| + | Thin:LT:fiche sidenw'shasth:cornitrol'oinf tthe'cramber. | ||
| + | If a bloc Loses members in coe electich and gains them in the next. the exiting stream may reioin. nereehily mem de • tS who sem. Othr7;dZs'!.°:7b7:::sh.rMelt =intcd | ||
| + | Tinted We. outlines mark the approomate rnember.ip of some of the smaller pot.. | ||
| + | HOW IDEOLOGY IS CALCULATED | ||
| + | Each member of Congress is assigned to an 'ideological category usrig DWNOMINATE a stat.ical system created by political scientists Keith Poole and Howard Rosenthal This system rat. each member of Congress's idedegical poshion positich based ch their votes. DWNOMINATE is pure, mathematical and involv. no judgernent co the content of bilk Instead.rnembers of Ccogress are placed ch a spectrum based ch how consistent, they vote together. VVhAe people argue that ideology is rrany-dimen,onal. Poole and Rosenthal found that nearly all Congres,onal voting | ||
| + | predicted by using just coe ideological variable. This variable tums out to rough, arrespond to position ch | ||
| + | Because members of Cal,. have served in overlapping terms with past members in a chain badcto the frst Congress.the system dm. comparisch of irfeology across | ||
| + | .11_ (Note: Scores are ccmparable across time but not between chambers, | ||
| + | F....de... Fn. | ||
| + | From the 1960s to the 1990s, conservative Southerners gradually left the Democratic Party while liberal Northerners moved the other way—reducing the ideological overlap between the parties and making each more homogenous. | ||
| + | Political scientists break US history into partisan eras called "party systems." Although the Fifth Party System (the New Deal Coalition) underwent this massive realignment in the 1960s and 1970s, they refuse to agree that the Fifth Party System has ended, because they can't point to a specific election where the realignment happened.This means we're now in the second part of the Fifth Party System, which seems like it might just be a political science Deathly Hallows/Breaking Dawn thing. | ||
| + | Voters in the early days of the Great Depression rallied around New York governor Franklin Delano Roosevelt, who united farmers, labor unions, academics, and minorities into the New Deal Coalition, whose slow disintegration was at the core of partisan politics for much of the 20th century | ||
| + | The late 1800s saw an obsessive focus on the issue of bimetalism that it took me a while to understand. | ||
| + | Farmers and poor people who owed money favored a dual gold-silver standard, because it would lead to inflation, which would make debts easier to pay off. Wealthy bankers—who owned that debt—wanted the opposite.This became the focus of a Main St. vs.Wall. St cultural struggle culminating in William Jennings Bryan's famous "Cross of Gold" speech. (Despite his fiery oratory, Bryan lost the presidential election to McKinley) | ||
| + | Politics in the first half of the 1800s was completely dominated by the issue of slavery, which was supported by poor white Southern farmers—Democrats—and opposed by the Northern Protestant intellectuals and wealthy businesspeople who formed first the Whigs and then the Republican Party. | ||
| + | During this period, as during the Civil Rights era, a second DW-NOMINATE variable becomes important, and corresponds to voting behavior on regional issues. If the first variable represents the left-right variable, then during these periods the second variable could simply be thought of as representing the racism spectrum. | ||
| + | The first divide in Congress was between supporters (right) and opponents (left) of the Washington Administration. --> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Trivia== | ||
| + | * The axis for the senate is mislabelled; on the right, it goes 0-10-20-30-40-50-'''40-40'''-80. | ||
| + | * This comic used to be [https://web.archive.org/web/20211215045721/https://store.xkcd.com/products/congress-poster available as a poster] in the xkcd store before it was [[Store|shut down]]. | ||
{{comic discussion}} | {{comic discussion}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:Comics with color]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Large drawings]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Charts]] | ||
[[Category:Politics]] | [[Category:Politics]] | ||
| − | [[Category:Comics with | + | [[Category:Comics with xkcd store products]] |
| − | [[Category:Comics with | + | [[Category:Comics with lowercase text]] |
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Comics featuring Joe Biden]] |
Revision as of 17:47, 9 January 2024
| Congress |
| ↓ Skip to explanation ↓ |
 Title text: It'd be great if some news network started featuring partisan hack talking heads who were all Federalists and Jacksonians, just to see how long it took us to catch on. |
Click the date above the comic to go to the xkcd page, and there is a link to the much larger version.
Explanation
It appears that the (at the time) upcoming 2012 election has put Randall into a political state of mind, as this is the second comic in a few weeks that has dealt with political history (1122: Electoral Precedent). As with that comic, this comic goes through the entire history of the U.S. Federal Government. Also notably, Randall makes a number of observations that are akin to the type of observations Randall denounces in 1122 (e.g. for 1928, Randall notes that no Republican has since won the presidency without a Nixon or a Bush on the ticket). Just around the election he posted two more comics related to this: 1130: Poll Watching and 1131: Math.
U.S. Federal Government
In the U.S. Federal Government, one of the checks and balances is a bicameral United States Congress, which consists of two "houses": the Senate, its "upper" house; and the House of Representatives ("the House"), its "lower house". The Senate consists of 2 senators elected from each state (thus 100 total), while the House consists of 435 voting representatives (a number decided upon in 1911 by law) whose apportionment is split between the states proportional to their population; although each state gets at least one (the House also has non-voting representatives from non-state territories like Puerto Rico and the District of Columbia). Every ten years, the House is reapportioned based on the latest census. The most populous state as of 2012 is California which has 53 seats in the House. Senators serve 6-year terms with elections held every 2 years for one-third of the seats. Members of the House (called Representatives or Congressmen/women) serve 2-year terms with all of the seats contested every 2 years.
In order for a bill to become a law, it must be passed by both the House and the Senate. In a way, this theoretically ensures that the bill is supported both by the majority of states (the Senate), and the majority of the population (the House). The President may then sign the bill into law, he may "veto" the bill, or he may do nothing, in which case it becomes a law if and only if Congress is in session after a waiting period of 10 days (not including Sundays).
Political ideologies
In politics, there is a scale that represents the political beliefs of a politician. The scale goes from "left" to "right" of "center" — which generally describes a balancing point of beliefs (sometimes called "left-wing" or "right-wing").
The "left" is a general belief in social justice, and is sometimes associated with socialism. Modern left-wingers generally prioritize equality, and support policies like welfare and government-subsidized healthcare. This trends toward having a larger federal government. In the U.S., "liberal" is a term often used to denote left-leaning tendencies.
The "right" generally believe in personal responsibility and individual liberty, which is often termed conservative. This trends towards having less regulation and thereby a smaller federal government. The goal is to keep the nation stable, and reducing the interference by the government with a person's wealth. This ostensibly means lower taxes, because the government does not provide as much.
Politicians typically align themselves into groups of similar beliefs and positions called "parties". In the U.S., there have generally been two dominant parties, although there have been times where three or more parties have shared roughly equal influence and support. In today's politics (which is apparently known as (the second part of) the fifth era of political parties, or Fifth Party System, as noted on the outside edges of the comic) of the two current primary U.S. political parties, the Democrats are the left-leaning party, and the Republicans are the right-leaning party. The dominant parties are generally considered "moderate" in their left- or right-wing leanings, as either party appears to requires the support of a majority (or a few percent under) of voters to win. However, this is complicated by a process called gerrymandering where election boundaries are redrawn to allow a political advantage to the party currently in power. Thus a popular majority state wide or any ratio of votes to representatives will not necessarily be reflected in delegates awarded, an example being the Republicans' REDMAP 2012 report ([1]). Smaller parties often run candidates with more extreme views, but such candidates rarely win, due to a more limited number of possible supporters ensuring that even a relatively large minority would have zero chance of representation. (see Duverger's law).
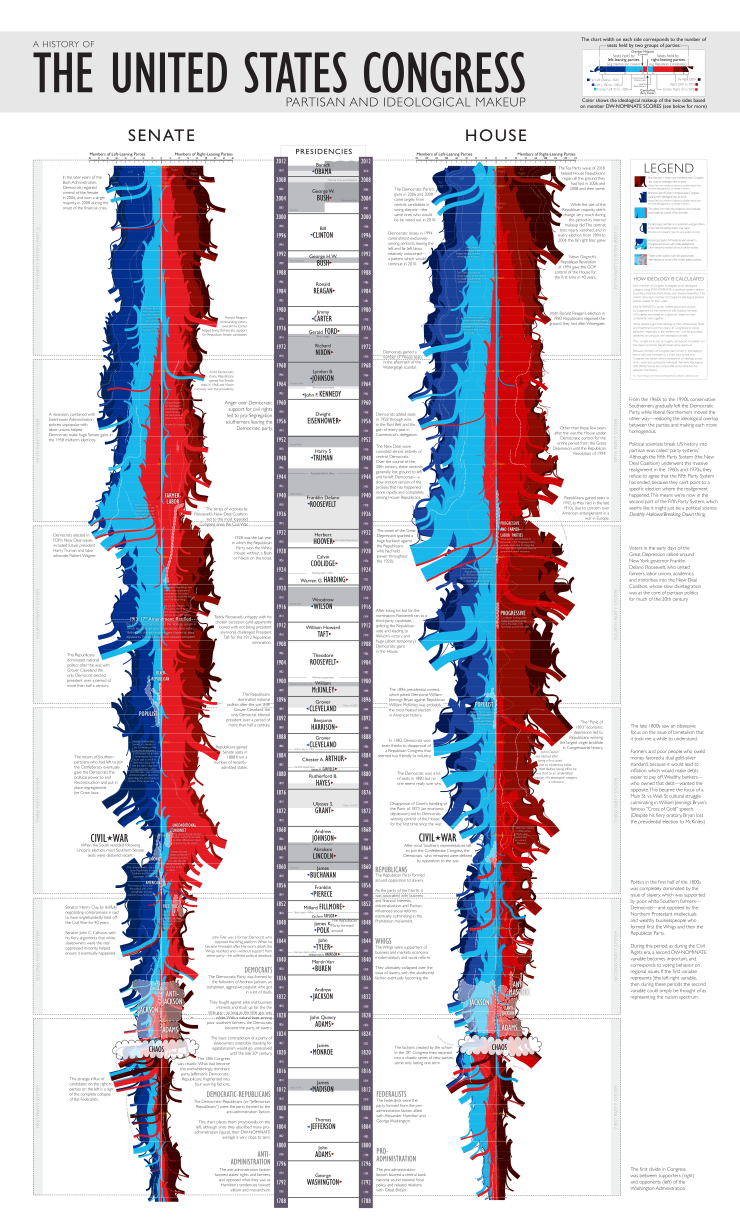
The comic
The comic effectively consists of three separate charts: The left- and right-hand charts are the main charts; they represent the Senate and House respectively, and purport to show the left- and right-wing leanings of each legislature through U.S. history. There is a legend on the right that sets out fairly clearly how the charts work, but basically Randall has split each wing into three levels including the very moderate or "Center" right or left, and the more extreme or "Far" right or left, as well as the average left and right without prefix. A dotted yellow line represents the balance of power in each legislature, and white lines represent the leanings of certain notable people including presidents.
Some presidents are not indicated, because they were never senators or congressmen (most of these were state Governors, such as Clinton, Bush and 2012 candidate Mitt Romney). As may be noted from the chart, Barack Obama is considered "left" while Paul Ryan is considered "far right". It's also notable that the "center right" ideology appears to be completely eradicated from the House and is waning in the Senate (although a similar trend is shown around 1900 with the centrists making a comeback thereafter).
On either side of these charts, there are descriptions or explanations for expansions and contractions of each ideological group.
The center chart appears to primarily act as a timeline. Each president is listed with their leanings indicated by a left or right arrow. Wars are shaded in grey. Other notable events are also indicated. On either side of the center chart (although somewhat mixed in with the aforementioned Senate/House explanations), there are also references to the primary parties of each era showing how they evolved (left-leaning parties on the left, and right-leaning parties on the right).
Finally, there's a little extra commentary on the right side, below the legend.
The title text
The title text refers to two political parties in American history: the Federalists and the Jacksonians.
Note that this means the two parties are not strictly contemporaries. There are features of both the modern Republican and Democratic parties in each, so depending on the topic presented, it may take a long time to figure out that they are not these modern parties until the topic of discussion changes. They do, however, make a nice dichotomy.
The Federalists are one of the oldest political parties in American History. Federalists were seen as conservative in their time, and similarly to modern Republicans much of their support came from bankers and businessmen and they were committed to a fiscally sound and government, but on the flip side they favored a strong central government, regulation of industry, a national banking system, and were protectionistic.
The Jacksonian party is one of the four branches of the Democratic Party that developed during the political chaos after the Federalist party died out in the War of 1812. The Jacksonians were considered liberal for their time, they believed in one man, one vote, regardless of standing, and their mascot was a donkey and they're the ancestors of the modern Democratic Party, but on the flip side they did not want a strong national government and believed that the government should have limited impact in the regulation of industry, going so far as to end the bank of the United States, and were fiercely expansionistic.
Network news channels regularly feature talking heads, supposed 'experts' who offer their opinion on the topical political stories. Where these talking heads are strongly aligned with a particular party, and are unconcerned with anything other than winning, they could be described as a partisan hacks.
Transcript
| |
This transcript is incomplete. Please help editing it! Thanks. |
- A history of
- The United States Congress
- Partisan and ideological makeup
- [The comic is divided into three massive sections, SENATE, PRESIDENCIES, and HOUSE. Timelines run backwards down the page between each section. In the HOUSE and SENATE sections, shifting, curving red and blue areas of different brightness illustrate the shifting balance of power between "Members of Left-Leaning Parties" and "Members of Right-Leaning Parties". Under PRESIDENCIES, different administrations are labeled and wars are shaded in gray. There are notes throughout all sections.]
- [There are additional notes on the right.]
- LEGEND
- [Square containing ribbons of color merging upwards with larger areas]: Branches join in when new members enter Congress and cause an ideological bloc to grow. (Note: If the new member is elected as another retires from the same ideological bloc, no change is shown.)
- [Square containing ribbons of color splitting off from larger areas]: Branches split off when members leave Congress, causing their ideological bloc to shrink. (Note: If the new member is elected as another retires from the same ideological bloc, no change is shown.)
- [Square showing yellow dotted line crossing from red to blue area]: The yellow line marks the midpoint, which indicates which side has control of the chamber.
- [Square in which curve briefly separates from blue area]: If a bloc loses members in one election and gains them in the next, the exiting stream may rejoin. This does not necessarily mean the same people returned.
- [Square showing white dashed line labeled Lyndon Johnson on top of ribbon merging with main area]: Future (and past) US Presidents who served in Congress are shown with white dashed lines. Other noteworthy members are shown with thin solid lines.
- [Square in which tinted area marked "Whig" sits over mix of red and blue areas]: Tinted white outlines mark the approximate membership of some of the smaller political parties.
- HOW IDEOLOGY IS CALCULATED
- Each member of Congress is assigned to an ideological category using DW-NOMINATE, a statistical system created by political scientists Keith Poole and Howard Rosenthal. This system rates each member of Congress's ideological position position [sic] based on their votes.
- DW-NOMINATE is purely mathematical and involves no judgement on the content of bills. Instead, members of Congress are placed on a spectrum based on how consistently they vote together.
- While people argue that ideology is many-dimensional, Poole and Rosenthal found that nearly all Congressional voting behavior - especially in the modern era - can be accurately predicted by using just one ideological variable.
- This variable turns out to roughly correspond to position on the classic economic liberal/conservative spectrum.
- Because members of Congress have served in overlapping terms with past members in a chain back to the first Congress, the system allows comparison of ideology across time - even accounting for individual members' ideological drift. (Note: Scores are comparable across time but not between chambers.)
- For more detail, see Poole and Rosenthal's website, voteview.com.
Trivia
- The axis for the senate is mislabelled; on the right, it goes 0-10-20-30-40-50-40-40-80.
- This comic used to be available as a poster in the xkcd store before it was shut down.
Discussion
Being a stupidly over political (please don't ask me here, this is an xkcd wiki not reddit) kinda guy, this one really interests me. Another one of those amazing visualizations of real-world facts xkcd is so great at. I have no idea what one might write for an explanation that would be useful. Everything is explained in pretty thorough fashion right on the panel... -- Renegade4dio (talk) (please sign your comments with ~~~~)
- Well, there's always the transcript for us to
waste timework on. Davidy22 (talk) 12:36, 29 October 2012 (UTC)
The first thing that is missing is the explanation why there are two houses. Why never three or four? I get why monarchy only had advisors but opposition varied with whichever branch of the family had most to lose. So there was a never ending and closely focussed stream of opposition, albeit short-lived if unsuccessful. I used Google News BEFORE it was clickbait (talk) 18:29, 15 January 2015 (UTC)
- Congress as check
Perhaps a pedantic point, but I couldn't leave the description describing Congress as simply a check on the president. That would imply that the president has free reign (literally) and that Congress only acts (or, more often, doesn't act) to veto the president. That is a much more accurate description of the president's role in legislation (or of a pre-modern English Parliament). -- 208.32.120.10 (talk) (please sign your comments with ~~~~)
- Typo
There's a typo on the right-hand side of the comic around 1952 - "Other than these few years after the war; the House [was] under control Democratic control for the entire period ...". The "was" is missing. TheHYPO (talk) 15:27, 29 October 2012 (UTC)
- definition of conservative is pejorative
Conservatives are not interested in preserving wealth amongst those who have it - they are interested in creating as many opportunities to create wealth as possible by reducing unwanted government regulation and returning to constitutional limitations (aka 10th ammendment) on Federal power. A different view of liberty and rights than what liberals maintain, but highly supported - I find your definition to be highly pejorative. Ghaller825 (talk) 18:59, 29 October 2012 (UTC)
- That went completely over my head, but you're entirely welcome to change it if the definition in the article bothers you. Davidy22(talk) 09:16, 30 October 2012 (UTC)
- Perhaps the segment could be changed to say "conservatives believe the government should not interfere with a person's wealth", or something very similar. The resistence to government involvement seems to be more consistent across the various degrees of the modern conservative movement. I'll admit that my suggested statement is also false, because almost everyone believes there should be some amount of taxes, and taxes affect wealth. However, it should be more palatable to the political ideology.
- I understand your offense, Ghaller. On the other hand, the current phrasing using "making wealth" is also a loaded term, as many factory workers would feel that they are "the ones who make it" more than the CEOs, but are certainly not getting more money. I'm not saying I agree with that perspective, just that it's a suggestive statement, and this is not the forum to have an endless debate over it. The unsigned comment above me has the best compromise in my opinion, so I will implement it. - jerodast (talk) 18:12, 22 December 2012 (UTC)
- Errors
I notice the following: (1) George H.W. Bush is shown as serving in the Senate. He never made it to the Senate, just the House. (2) Abraham Lincoln appears to be shown as serving in the House for about seven years. He only was there for one term (two years). --99.14.234.119 02:18, 30 October 2012 (UTC)
It also lists John A. Garfield in the House from 1862 until his election -- it is James A Garfield, not John.
It lists Abraham Lincoln (and the Republican Party of Lincoln's time in general) as right-leaning, even though it's widely accepted that the Republicans of that era (whose base was made up mostly of Northern abolitionists) were the more liberal party, and the Democrats (whose base was comprised in large part by Southern slave-owners) the more conservative. -- 140.247.0.73 (talk) (please sign your comments with ~~~~)
- Definition of Liberal
While in the US, liberal might mean left-wing, in the UK it's pretty central and in Australia it's right-wing. Go figure.--Joe Green (talk) 04:23, 30 October 2012 (UTC)
- Classical liberalism [2] is very different from American liberalism; Americans would recognize it more as Libertarianism. --Prooffreader (talk) 09:12, 30 October 2012 (UTC)
The socialists are well-known for hijacking the good-sounding misleading names. Such as "liberal" in America or "bolshevik" (a made-up word meaning literally "majoritan", a member of majority) in Russia. 108.162.245.111 00:10, 24 January 2014 (UTC)
That comment makes it sound like there's some conspiracy behind the left thinking up good names for their movements. The words themselves don't really mean anything. You don't have to go back too far in US history to find 'liberals' and 'socialists' being demonized as spies and traitors, and even today the right is happy to call the left 'liberal' with strong undertones of 'weak'. Leftist are generally better at naming things I'll grant you, but then almost all leftist movements (barring the Khmer Rouge and cultural revolution era china) have had strong ties to both universities and the entertainment industry, people who are used to being persuasive with words so it's not surprising that they came up with nice friendly sounding terms for their movements.LostAlone (talk) 12:17, 6 April 2015 (UTC)
- Typo
In the "How Ideology Is Calculated" section, I note "acccounting".--Joe Green (talk) 04:23, 30 October 2012 (UTC)
- Conservative?
He didn't exactly say that Conservatives are interested in preserving wealth amongst those who have it; I think the implication is that "if you made it, you should get to keep it" (or as much of it as possible, hence lower taxes). One consequence of this is that the distribution of wealth tends to remain static, in that the rich stay rich and the poor stay (relatively) poorer. Whether or not that consequence is an intentional one is perhaps in the eye of the pejoratively-inclined beholder :-)--Joe Green (talk) 04:30, 30 October 2012 (UTC)
- I made an edit to that effect, but it appears to have been wiped out by another editor calling it "right-wing trolling". If you would like to try re-wording it, please do. lcarsos (talk) 05:05, 30 October 2012 (UTC)
- Arteries
Kind of unrelated but the diagram to me looks sort of like arteries and veins, with the red and blue. And the branches look like how they branch off the heart and stuff. Bugefun (talk) 05:10, 31 October 2012 (UTC)
- Red inside blue and vice versa
What do the red strands inside the blue section and the blue strands inside the red section represent? It doesn't seem to be explained anywhere. 199.27.200.82 14:15, 31 October 2012 (UTC)
- Red on the blue side represents "Conservative Democrats" and Blue on the red side represents "Liberal Republicans". Confusing a bit, but so are both those political terms (lol). It is stated (in small text) on the top right diagram of the comic--Dangerkeith3000 (talk) 14:53, 31 October 2012 (UTC)
- Left vs right - or why this comic is stupid
The traditional definition of left vs right (people attribute all sorts of things to it these days) is the support of change (hence the names progressives vs conservatives, or radicals vs reactionaries). The terminology comes from France where those that advocated reforms to government sat on the left of the chamber and those that wanted to do such things as restore the monarchy sat on the right. Your traditional Burkian conservative (smidgen to the right of the centre) would accept change is inevitable, but must be controlled. To the right of that people that want to maintain the status quo, further right people that want to go back to some "better time". To the left you get the, let change happen as it comes, further left lets make change a "good thing", to the furthest left "lets force change". A large part of the Marxist philosophy is that not only is communism desirable, but inevitable as according to Marx that is the final destination of all societies. Now to my point. Over time the parties have switched sides and often will be left on one issue and right on another. Often the parties themselves were divided (look at the civil rights act's passage) To simply say Democratic Party has always been left and the Republicans have always been is such a gross simplification that is renders the whole image a farce. 192.43.227.18 01:07, 8 November 2012 (UTC)
- Does it matter? The interesting thing about it isn't left or right, it's the decline in the center. You could completely flip it and it would make little difference. DanielLC (talk) 00:18, 8 November 2024 (UTC)
- What can we learn from this?
I've learned that our congress (and law in general) is too complex. We are tying to keep outdated laws relevant by using an endless series of exceptions (legally called amendments). I hope someday we will be able to scrap the whole thing and simplify our laws so that our children do not have to spend up to a quarter of their lives learning our mistakes. XKCD, please help us simplify something like law so you don't have to waste your time visualizing something as broken as our understanding of it. - e-inspired 24.51.197.187 18:36, 27 February 2013 (UTC)
This is something someone needs to contact Randall about. 108.162.219.105 (talk) (please sign your comments with ~~~~)
- Mesage of the day
Yes. We desperately need to fix the Congress... -- Wesha (talk) 19:39, 11 May 2015 (UTC)
It might help to have a corollary chart that tracks gerrymandering, that is the practice of selecting and isolating minority and majority populations in districts so that there is virtually no contest at the time of election. A city can be carved up to include just enough suburban voters to overwhelm what would otherwise have been their political choice. Districts now often resemble convoluted, sinuous serpent creatures rather than geography divided along natural boudaries. If someone could write code that would redraw districts with the following parameters: number of voters, and walking distance to polling places - without regard to income, race, party designation, etc. It would change the map drastically. At any rate, many districts have been redrawn to control election results. Such a chart would parallel the divisions in congress.Bralbovsky (talk) 00:25, 15 May 2015 (UTC)
Someone could (and probably has) come up with code to do what you suggest, but the courts won't let them use it.
When districts are drawn without regard to race, some racial groups wind up underrepresented, because they are a substantial percentage of the total population, but are not a majority in a proportional number of districts (for example, if there are 4 districts and they are 25% of the total populations, then they should be able to elect someone from that group in 1 district, but if they are 25% of each district, then members of the other racial group, which is 75% of each district, may get elected in all 4 districts, when it should be just 3). This is considered unfair and a violation of their right to "equal protection", so districts must be drawn along racial lines to comply with court orders to give these groups fairer representation.
108.162.215.190 16:50, 24 May 2015 (UTC)
Not intending to worry anyone, but isn't it annoying that the colours are the wrong way around? In the UK we represent the Tories/Conservatives/Republicans with blue and the Labs/labour/democrats with red. This is why it fits that the social democratic reforms promoted by social communism a flown on a red flag and the working capitalists and imperial monarchists are represented by a blue flag. Why the other way round? Raydleemsc (talk) 08:05, 25 May 2015 (UTC)
If this chart was about British politics, the colours would be wrong, but in US those are the standard colors for the parties. Blame mass media if you want [[3]] S42ky (talk) 18:51, 25 May 2015 (UTC)
- This is actually a pretty recent thing--and a silly one. Traditionally, each news outlet picked colors independently, and they were pretty evenly split among red for Republican or red for Democrat most years. In 2000, when the election was hung waiting on the Florida recount, everyone on TV was pointing at electoral maps on every broadcast. After two days, NBC switched colors. Other outlets began to follow suit, and once most outlets were using the same color scheme, after which pundits started talking about "red states" and "blue states" as shorthand for states where republicans or democrats won, and we've been stuck with that ever since. So, what made NBC change? Either their news director was annoyed that NBC and the Washington Post (the first paper he read in the morning) used opposite colors, or one of their pundits couldn't remember which colors they used and suggested that the alliterative red=Republican would help him stop screwing it up. Whichever of those is true is the ultimate reason red means Republican. 199.27.130.180 12:24, 18 September 2015 (UTC)
- It's a shame this chart doesn't get updated. It's going to need some infrared ink over the next 4 years! SteveBaker (talk) 14:27, 13 December 2016 (UTC)
- Our country is now led by a GOP monopoly... :( If only Sanders had won the Democratic nomination, we might not be in this mess. 108.162.238.17 03:19, 31 January 2017 (UTC)
- It would be interesting to see a more updated version of this at this point. Never understood US politics, but I'm under the impression your colour amounts would be looking different over the last few years. 162.158.7.97 22:09, 5 January 2021 (UTC)
- Our country is now led by a GOP monopoly... :( If only Sanders had won the Democratic nomination, we might not be in this mess. 108.162.238.17 03:19, 31 January 2017 (UTC)
There are a lot of "bent texts" that are missing from the transcription. (citation needed) ConscriptGlossary (talk) 13:24, 21 July 2024 (UTC)
- There's a lot of corrections to be made to the "OCR'ed" text (sic, shouldn't have an apostrope!), because it is not visible and forgotten. I spotted many spacing errors, for example, but whether it's worth the effort of going through that..?
- PS, it's {{Citation needed}}. Though doesn't really fit as either the normal (non-xkcd) or local contexts, so not sure why you tried to use it. 172.70.86.38 15:01, 21 July 2024 (UTC)
Is there an updated version of this? I feel like partisanship has only gotten worse since this comic was made. DanielLC (talk) 00:18, 8 November 2024 (UTC)
